
IV Therapy for Crohn’s & Ulcerative Colitis
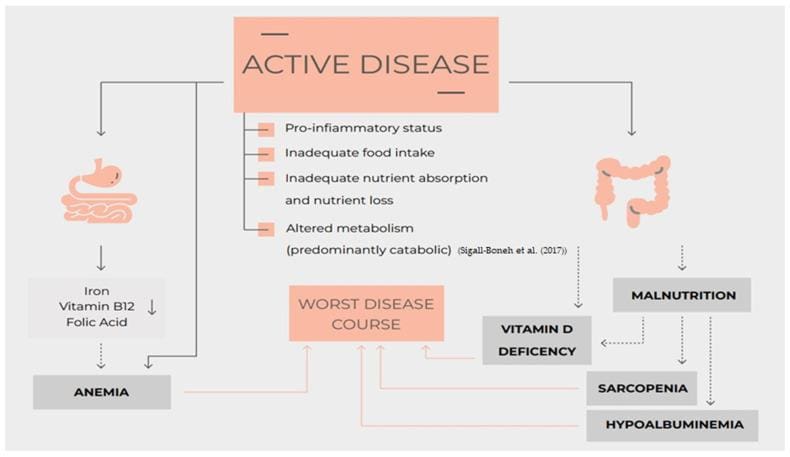
Malnutrition is surprisingly common in people living with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Between active inflammation, poor nutrient absorption, and digestive discomfort, getting enough nutrition can be a real challenge — even for people who eat a balanced diet or maintain a healthy weight.
In this blog, we’ll explore why nutrient deficiencies are so common in IBD, which vitamins and minerals are most often lacking, and how IV therapy for IBD can help restore your body’s nutrient balance and energy levels.
Why Malnutrition is Common in IBD (Crohn’s & Ulcerative Colitis)
People with IBD face several unique challenges that make nutrient deficiencies more likely:
- Poor absorption – Inflammation in the gut (especially in the small intestine) reduces the body’s ability to absorb nutrients.
- Increased nutrient needs – During active inflammation or healing, the body requires more vitamins, minerals, and protein.
- Food avoidance and appetite loss – Many people avoid certain foods to prevent symptoms, which can reduce dietary variety and intake.
- Medication effects – Some IBD medications (like corticosteroids and sulfasalazine) can interfere with nutrient metabolism or absorption.
- Frequent diarrhea or bleeding – This can cause direct nutrient loss, especially of iron, zinc, and electrolytes.

Common Nutrient Deficiencies in IBD — and How IV Therapy Can Help
| Nutrient | Why It’s Low in IBD | Symptoms or Risks | Available in IV Therapy? |
| Iron | Blood loss, poor absorption, inflammation affecting metabolism | Anemia, fatigue, brain fog | Specialty iron infusions (not through naturopaths) |
| Vitamin B12 | Malabsorption in the terminal ileum (common in Crohn’s) | Fatigue, memory issues, anemia, tingling/numbness | ✅ Yes |
| Folate (B9) | Malabsorption, medication effects (sulfasalazine) | Fatigue, anemia, mood changes, birth defects in pregnancy | ✅ Yes |
| Vitamin D | Fat malabsorption, inflammation, low intake | Bone loss, fatigue, lowered immunity, mood issues | IM injection (not IV) |
| Zinc | Losses from diarrhea, poor intake | Hair loss, slow healing, weakened immunity | ✅ Yes |
| Magnesium | Losses from diarrhea or medications | Muscle cramps, fatigue, low energy | ✅ Yes |
| Selenium | Poor absorption, low intake | Weak immunity, thyroid issues, oxidative stress | ✅ Yes |
Why Nutrient Replenishment Matters in IBD
Our bodies need vitamins, minerals, and electrolytes to produce energy, support healing, and maintain strong immunity, bones, and muscles. In IBD, nutrient deficiencies can:
- Increase fatigue and brain fog
- Delay wound healing
- Worsen inflammation
- Lead to anemia or bone loss
- Affect mood, memory, and nerve function
Addressing nutrient deficiencies is a foundational step in IBD management — helping patients feel stronger, recover faster, and improve quality of life.
Benefits of IV Therapy for IBD Patients
IV nutrient therapy delivers vitamins and minerals directly into your bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system. This makes it especially helpful for people with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis who experience poor absorption or active flares.
Advantages of IV therapy for IBD include:
- 100% absorption – Nutrients go straight into the bloodstream, ready for immediate use
- Bypasses digestion – Ideal for inflamed or irritated digestive systems
- Customizable formulas – Tailored to your specific deficiencies and symptoms
- Fewer pills – No need to take multiple supplements daily
- Support during flares – Helps replenish nutrients lost during diarrhea or reduced food intake
When IV Therapy May Be Recommended
You might benefit from IV therapy if:
- You’re not responding well to oral supplements
- You have ongoing nutrient deficiencies
- You’re experiencing active inflammation and absorption issues
- You have frequent diarrhea or bleeding
- You feel too unwell to eat or keep food down
IV Therapy vs. Enteral Nutrition in IBD
Enteral nutrition involves feeding through a tube placed into the stomach or small intestine, delivering a nutrient-rich formula. It’s often used in children with IBD and can reduce inflammation as effectively as corticosteroids.
However, access to enteral nutrition is limited outside hospital settings. While IV therapy does not replace the calories and protein provided by full enteral nutrition, it can be a more accessible option for replenishing vitamins and minerals when eating or digesting food is difficult.
Final Thoughts
If you live with Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis and struggle with fatigue, low energy, or recurring nutrient deficiencies, IV nutrient therapy may help bridge the gap — especially when your digestive system needs a break.
Curious if IV therapy is right for you? Book a complimentary discovery call to learn how we can customize your treatment for your IBD needs.
FAQs About IV Therapy for IBD
1. What is IV therapy for IBD?
IV therapy delivers vitamins and minerals directly into your bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system — ideal for people with nutrient absorption issues due to IBD.
2. Is IV vitamin therapy safe for Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis?
Yes, when administered by a licensed practitioner. Formulas are customized to your nutrient needs and health status.
3. Which nutrients can be given through IV therapy for IBD?
Common options include vitamin B12, folate, magnesium, zinc, and selenium. Vitamin D is typically given as an injection rather than IV.
4. Does IV therapy replace the need for a healthy diet?
No — it complements your nutrition plan, especially during flares or when absorption is compromised.
Reference:
Valvano, Marco et al. “Nutrition, Nutritional Status, Micronutrients Deficiency, and Disease Course of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.” Nutrients vol. 15,17 3824. 31 Aug. 2023, doi:10.3390/nu15173824
PMID: 37686856



